Thanks to power sharing and load balancing for electric vehicles, EV chargers will be able to safely power more than one EV per home. As more people adopt EVs, they’ll be needing better charging technology to charge two vehicles at once, for example.
Today, we introduce these functions, explain how they work, illustrate them with examples, and list some of the benefits and advantages of having these features on your EV charger.
Power Sharing
What Is Power sharing?
Most Australian homes feature a single-phase electrical connection with an electrical capacity of up to 63A. In most cases, homes can easily power your stock standard charger that requires 32A, but charging two EVs simultaneously using separate chargers is a slightly more complex process.
Powering two level 2 EV chargers that both require 32A, would require you to dedicate the entire electrical infrastructure of the home to EV charging (as using our example above of a standard house having 63A, 32×2 = 64A). In most cases, you would not even be able to turn your lights on. This is where EV charging with power sharing comes in.
Power sharing allows you to set up a maximum power input for each of the chargers you install (i.e. if you install 2). This means that in a 63A home, you could configure the 2x EV chargers to demand a maximum of 40A, leaving you with 23A to spare for powering regular appliances. This is an energy management feature that allows you to maximise EV charging capabilities for two electric vehicles with the same electrical capacity, while controlling the power demand within safe a range for the electrical system.
However, you should keep in mind that with power sharing you are essentially manually assigning a maximum capacity to be used by the EV chargers. This will leave a maximum capacity for you to be used on other appliances that you must not exceed in order not to trip the main circuit breaker. In our previous case example, you should be careful not to exceed the 20A for each charger.
How Does Power Sharing Work?
When EV charging with power sharing is active, the shared load of all connected EV chargers will not exceed the maximum capacity set by the user. This allows you to safely charge two EVs simultaneously and use appliances at home as you regularly do.
The way EV charging with power sharing works is the following:
All connected EV chargers are communicating via Wi-Fi or Ethernet. When a single charger is active, it can charge the EV at full capacity with no problems to the electrical infrastructure of the home. When the second EV is connected, both chargers will monitor the charging rate and limit the shared load to the configured maximum capacity, set by the user.
Power Sharing Practical Example
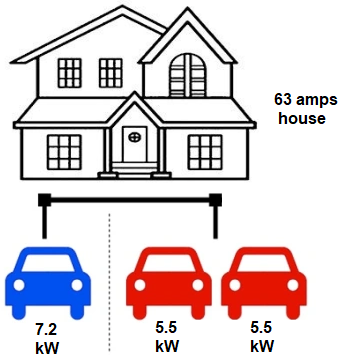
Let us better understand this feature with an example.
For EV charging with power sharing let us consider a home with a 63A electrical capacity and two 7.2kW single-phase EV chargers connected to different circuits. In this case, the homeowner wants to set 48A for EV charging and leave 15A available to power other appliances in the home while EV charging.
When only one EV is connected, the charger will supply full power, drawing 32A. After the second EV is connected, both chargers communicate and the load is distributed equally between EVs, leaving 24 amps per EV to deliver a charge rate of 5.5kW for each of them.
If the family installed two EVs without power sharing capabilities, they could only charge a single EV at full rate since as soon as the second electric car is connected (demanding 32A), the main circuit breaker of the house would trip. This would interrupt the charging process and result in a poor user experience. The alternative approach in this scenario would be to upgrade the cut-out fuse to 80A or even 100A if allowed by the utility. This could be a longer permit process and could involve extra expenses in electrical infrastructure upgrades. We usually don’t recommend this as it’s quite costly.
Load Balancing
What Is Load Balancing?
Many people confuse power sharing with load balancing. This function is relatively similar to EV charging with power sharing since it adds a layer of flexibility to the EV charging process by considering the limited electrical infrastructure of the home, but there are two main differences between them.
- Load balancing considers the electrical capacity of the home and automatically adjusts the charging rate to fit within the availability power capacity at any given time.
- Load balancing can be used when charging a single EV or multiple electric vehicles.
One of the useful applications of load balancing is when you have high demand load applications at home such as heat pumps, electric showers or washing machines. These appliances demand a lot of power, which is why using them in combination with an EV charger could potentially result in tripping the main circuit breaker (even if you are charging a single EV). By integrating load balancing into the equation, your system will reduce EV charging accordingly to safely supply power to these other appliances as needed.
In summary, load balancing for electric vehicles is a function that dynamically balances the load of the EV charger (or chargers) and the load demanded by all active appliances in the house to fit within the electrical capacity of the home.
How Does Load Balancing Work?
The way load balancing works for EV chargers is very interesting.
First, a separate energy management device measures power demand at the home considering all connected appliances to the service panel. This dynamic energy monitoring works like a smart metre that is connected as well to the EV charger. This needs to be installed by a qualified electrician.
While the energy management device reads the energy usage at the home, the charger demands a load equal to or lower than the remaining electrical capacity (after factoring in the consumption for all appliances). In other words, the other appliances of the house are prioritised over EV charging.
Load Balancing Practical Example
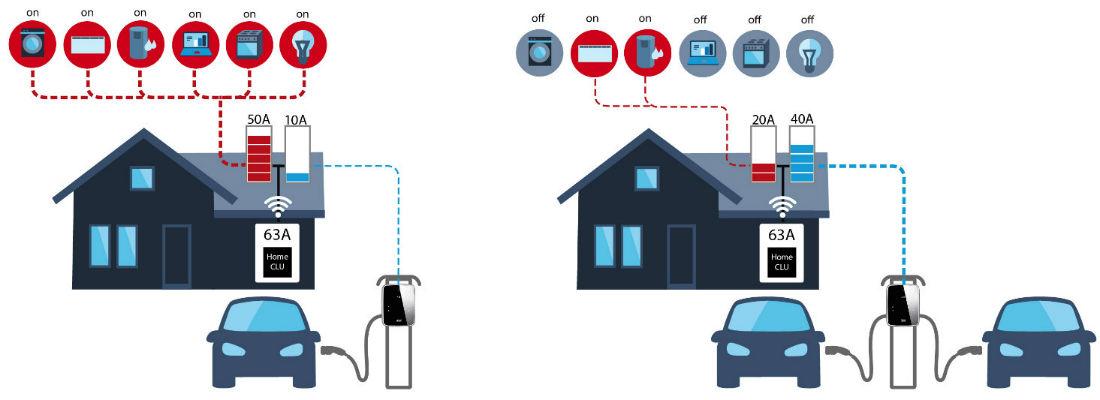
For this example, we will examine how the system will behave for the same home in different times of the day. For the first case, let us consider a morning time with a single EV at home (figure 3.a), while for the second case, let us consider a night time with two EVs connected to the house (figure 3.b).
In figure 3.a, only one EV is connected, but the family is using all types of appliances and demanding around 50 amps in household consumption. This only leaves the EV charger with around 10 amps available, delivering a low charging rate of 2.3kW to the EV.
Then, at night (figure 3.b), a second EV is connected and the home appliances only demand a load of 20 amps as the people are sleeping. In this case, an available capacity of 40 amps or 9.2kW is left available to share between the two electric cars. Depending on the programming of the charger, the power can be shared equally between EVs or adjusted according to the state of charge of each EV.
As can be seen, the system dynamically adjusts to the needs of the user depending on how many loads are connected and how many cars need to be charged. This ensures that protection devices will not unnecessarily trip due to excess demand.
Advantages of Load Balancing and Power Sharing Capabilities
Load balancing and power sharing are excellent functions. Some highly advanced EV chargers featuring load balancing capabilities include the Zappi EV charger and the Wallbox Pulsar Plus, while the Tesla Gen 3 EV charger features power sharing technology, all of which revcharge stock. You can shop our chargers on our store page.
When using load balancing and power sharing, you will be able to enjoy many interesting advantages. Some of the most important ones are the following:
- No need to upgrade the electrical infrastructure at your home.
- Families can own and charge multiple EVs simultaneously.
- High-consuming appliances (water pump, HVAC systems, and others) can be used with no fear of tripping the main breaker (load balancing exclusive)
- Load balancing for electric vehicles can be used in a workplace to offer EV charging to employees without compromising the power availability of the building. (Non-residential)
- EV charging with power sharing can be used to easily charge EV fleets. (Non-residential)
Read also- How Long Does an Electric Car Battery Last?